深入分析事务和 MVCC
深入分析事务和 MVCC
事务
事务:几个重要属性 ACID 以及原理
锁:乐观锁、悲观锁、行锁、表锁
MVCC:多版本并发控制
解决并发访问数据库系统时,提高读写效率,因为加锁以后会影响效率
MVCC
当前读:总是读取最新版本的记录
触发条件案例:
insert update delete修改之前都是要获取数据的
select ... lock in share mode这个也是当前读
select ... for update这个也是当前读。
快照读:读取历史版本的记录,历史版本记录在
undo log,回滚日志中触发条件案例:
select * from table
案例:
现在有 2 个事务 A 和 B
| A | B |
|---|---|
| select | select |
| Update commit | |
| select |
- 事务 A 先执行了查询操作,事务也执行了查询操作
- 事务 B 更新了操作,然后提交事务
- 事务 A 进行查询操作
最后事务 A 再查询能获取到事务 B 修改之后的内容么?
隔离级别
MySQL 是有不同的隔离级别的,在不同的隔离级别下是不一样的。
- 可重复读(RR):默认的隔离级别
- 读已提交(RC):就是事务 B 提交之后,事务 A 立即就可以读取到最新的数据
- 读未提交:不用了解,现在没有数据库采用此隔离方式
- 序列化:事务开启后,只允许一个人操作,相当于开启了一个单线程
所以在
RR隔离级别下:事务 A 是获取不到新数据的在
RC隔离级别下:事务 A 是可以读取到新数据的
MVCC 实现原理
隐藏字段
DB_TRX_ID:创建或最后修改记录的事务 ID
DB_ROW_ID:隐藏主键,当没有设置主键的时候默认就是这个
DB_ROLL_PTR:回滚指针,undo log指向上一个历史记录
案例:
事务 1 创建一条数据
| id | name | age | sex | DB_TRX_ID | DB_ROW_ID | DB_ROLL_PTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null |
第一次创建数据时,事务 ID 就是 1,隐藏主键和主键一样,因为数据刚创建,所以回滚指针是null。
事务 2 把name值修改为李四
| id | name | age | sex | DB_TRX_ID | DB_ROW_ID | DB_ROLL_PTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | null |
先把上面的数据保存到undolog中,然后再修改成李四,还要修改事务 ID 和回滚指针
| id | name | age | sex | DB_TRX_ID | DB_ROW_ID | DB_ROLL_PTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 李四 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0x11 |
回滚指针指向上面undolog的地址,然后这一条就成为了最新记录。
事务 3 把age修改为 31
| id | name | age | sex | DB_TRX_ID | DB_ROW_ID | DB_ROLL_PTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 李四 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0x11 |
然后和上面一样,先保存当前修改后的内容到undolog,然后再更新数据
| id | name | age | sex | DB_TRX_ID | DB_ROW_ID | DB_ROLL_PTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 李四 | 31 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0x12 |
当不同事务对同一条数据进行修改时,
undolog会形成一个链表,链首就是最新记录,后面都是历史记录。
当事务 4 来临时,获取到的是上面哪个值?
这就引出了一个readview概念,它是事务在快照读时产生的读视图,它保存了 3 部分:
trx_list:系统活跃的事务 IDup_limit_id:列表中事务最小的 IDlow_limit_id:系统尚未分配的下一个事务 ID
demo 实践查询
首先创建一个demo数据库,然后创建一个user表
create database demo;
create table user(id int not null primary key auto_increment, name varchar(100) not null default '', age int unsigned not null, sex int not null default 1);
然后我们查询一下事务的隔离级别
mysql> select @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
| @@tx_isolation |
+-----------------+
| REPEATABLE-READ |
+-----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql>
是RR级别,然后我们设置autocommit
mysql> set autocommit=0;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
我们开 2 个终端进行连接测试。
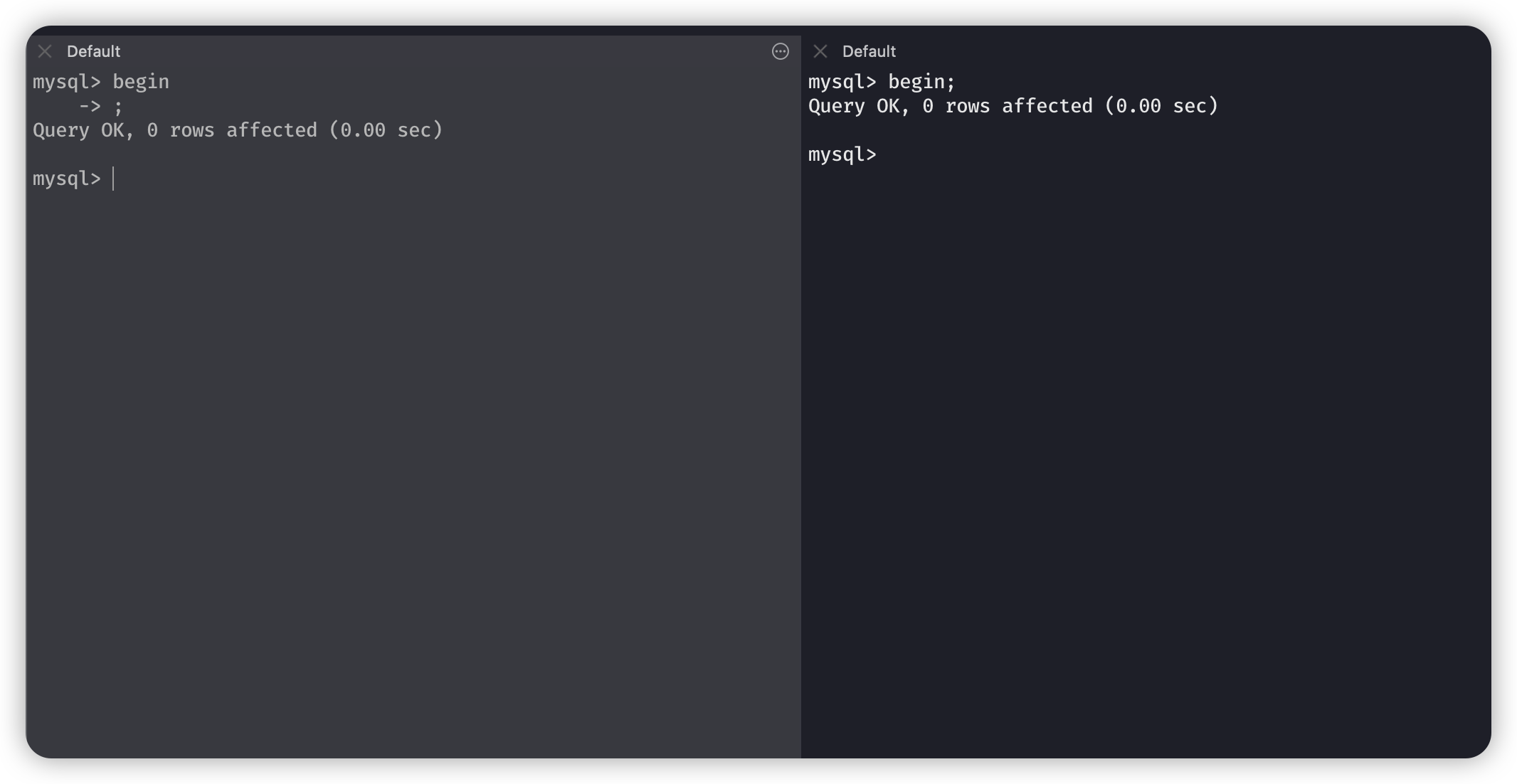
两个同时开启事务。提前准备一个数据插入进去。
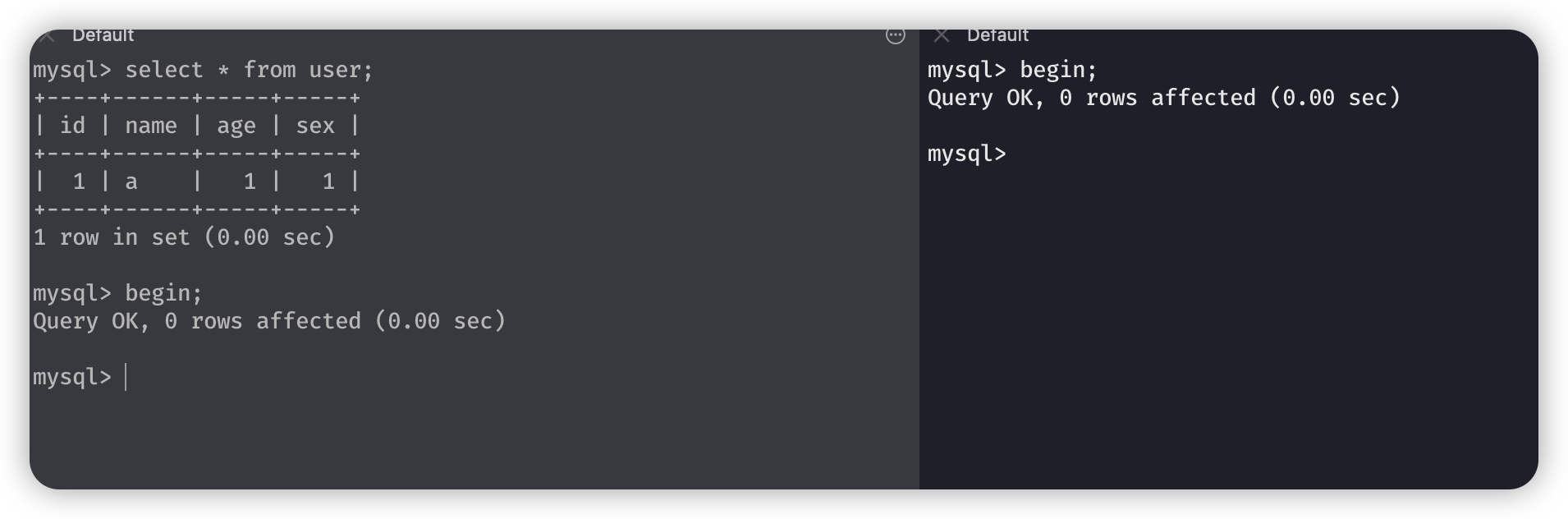
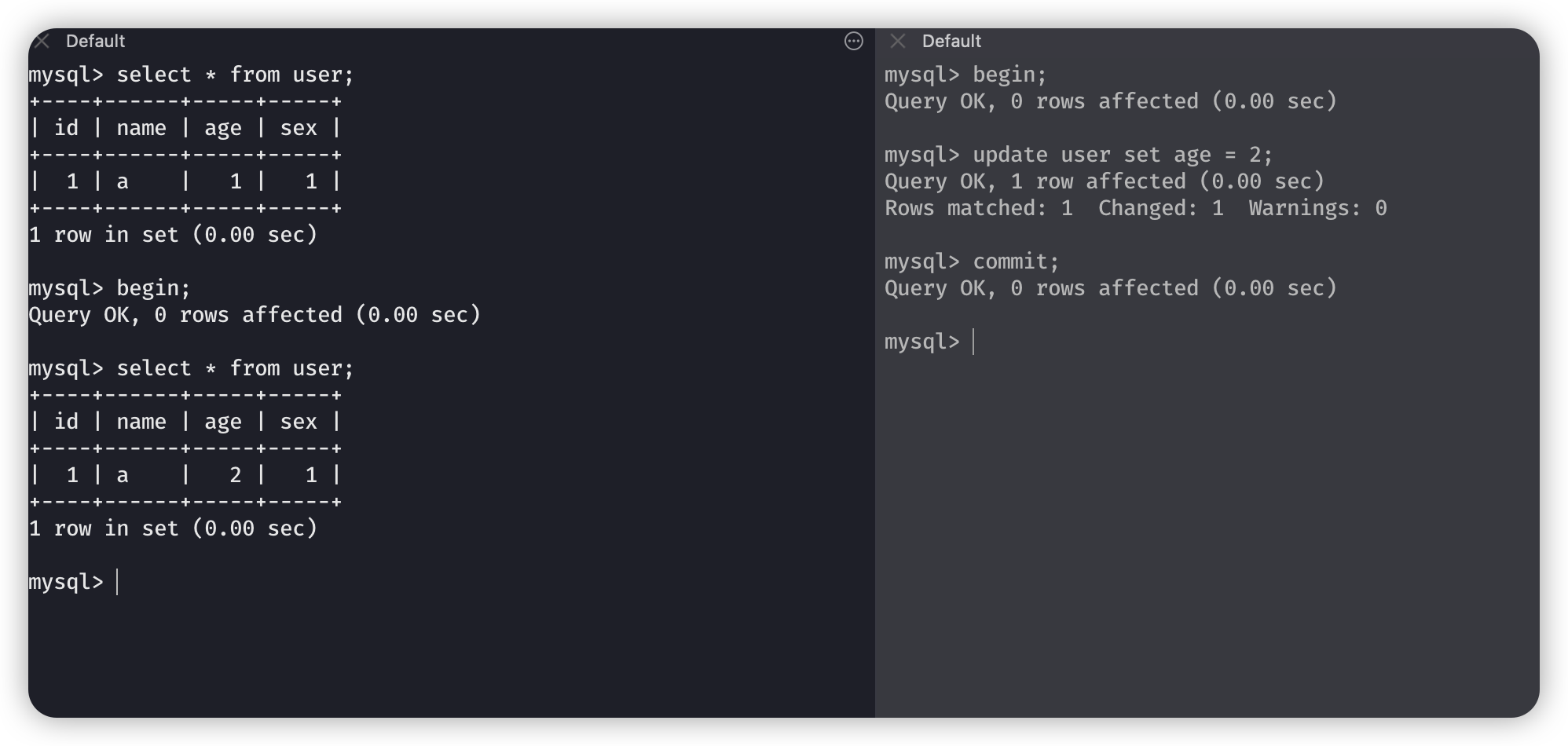
右边先更新了年龄为 2,然后提交,左边能够查询到更新的内容。
然后我们两个都commit之后,再重新都开启事务,都同时begin一下
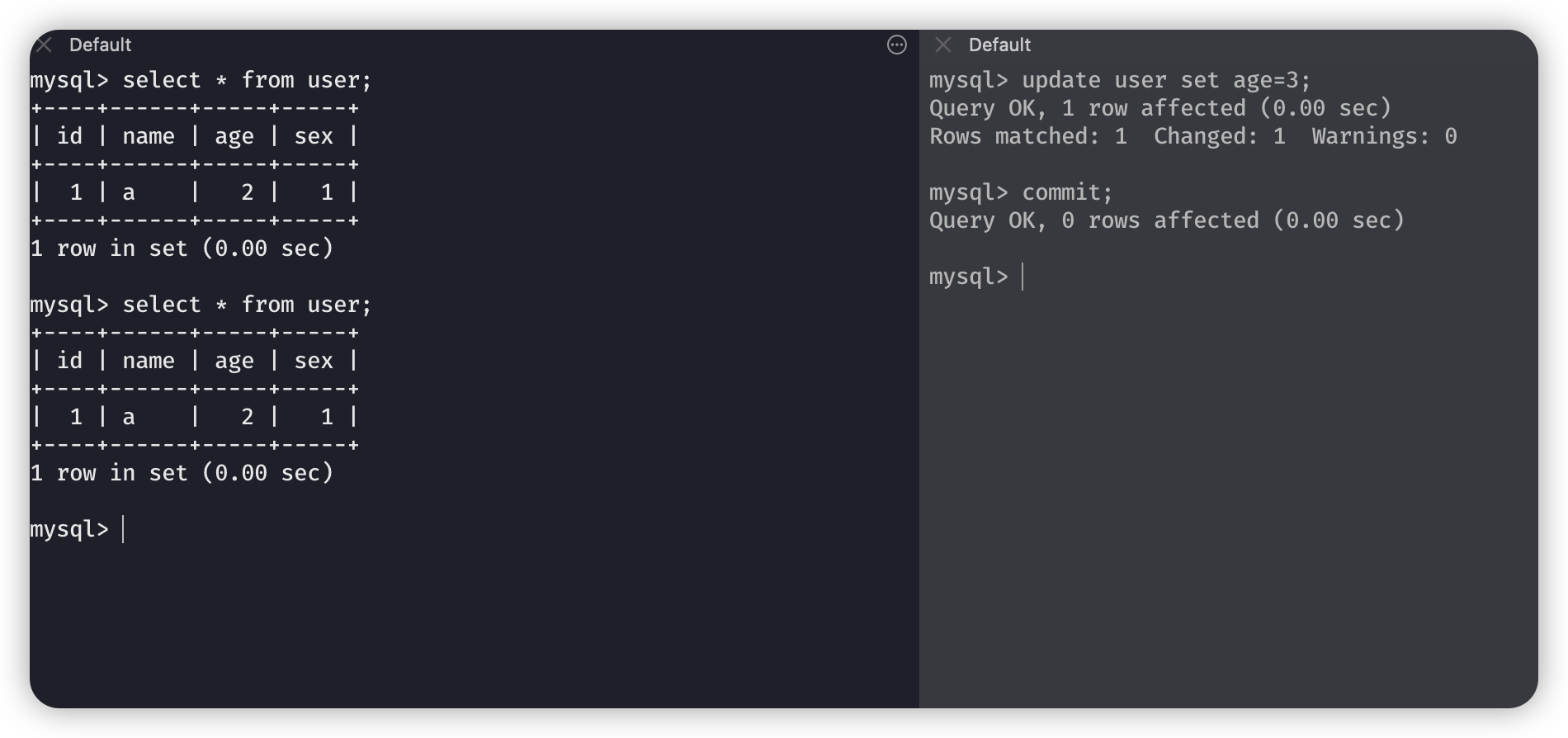
然后,左边的先查询一下,然右边的更新年龄为 3,进行提交,左边再进行查询,就查询不倒更新的内容了,只有当commit了之后才能查看到修改后的内容。
mysql> select * from user;
+----+------+-----+-----+
| id | name | age | sex |
+----+------+-----+-----+
| 1 | a | 2 | 1 |
+----+------+-----+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
+----+------+-----+-----+
| id | name | age | sex |
+----+------+-----+-----+
| 1 | a | 2 | 1 |
+----+------+-----+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
+----+------+-----+-----+
| id | name | age | sex |
+----+------+-----+-----+
| 1 | a | 3 | 1 |
+----+------+-----+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
这一次的区别呢就是,我们先在右边更新了,创建了快照读。
注解
- 比较
DB_TRX_ID和up_limit_id,如果小于,则当前事务能看到DB_TRX_ID的记录,如果大于和等于,则进入下一个判断 - 比较
DB_TRX_ID和low_limit_id,如果大于等于则代表DB_TRX_ID的记录在readview生成后出现的,那么对于当前事务不可见。如果小于,则进入下一个判断。 - 判断
DB_TRX_ID是否在活跃事务中,如果在,代表readview生成时,事务还在活跃状态,修改的数据当前的事务是看不到的,如果不在,说明事务在readview之前就commit了,那么修改的结果就是可见的。
| 事务 0 | 事务 1 | 事务 2 | 事务 3 | 事务 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| insert | 开启 | 开启 | 开启 | 开启 |
| update commit | ||||
| select |
- RC:每次进行快照读都生成读视图
- RR:只有第一次时生成读视图,之后每次使用都是第一次的读视图
解读步骤:
前 3 个都是快照读保存的信息,最后一个是最新的一次操作的事务的 ID
上面步骤演示的第一种情况
- trx_list:活跃的事务 ID,上面 1,2,3 都提交了,所以这里是 123
- up_limit_id:最小的是 1
- low_limit_id:下一个,现在是事务 4 提交了,所以下一个是 5
- DB_TRX_ID:最新的一次事务 ID 就是事务 4,所以是 4
上面演示步骤的第二种情况,我们先更新了用户的年龄,就先产了读视图,后查询的数据分析:
- trx_list:活跃的事务 ID,上面 1,2,3,4 都提交了,所以是 1234
- up_limit_id:最小的是 1
- low_limit_id:下一个,现在是事务 4 提交了,所以下一个是 5
- DB_TRX_ID:这次是 0,因为都没有进行操作,当事务 4
update and commit之后,上面都不变,4 执行完之后就变成了 4
然后根据上面的注解进行套用判断:
- 第一种情况就是可见的
- 第二种情况事务还在活跃状态,就是不可见的,再等到下一次
commit之后就可以看到了。
幻读
同一个事务中,不同的时间,两次相同的查询获取到的数据不同。
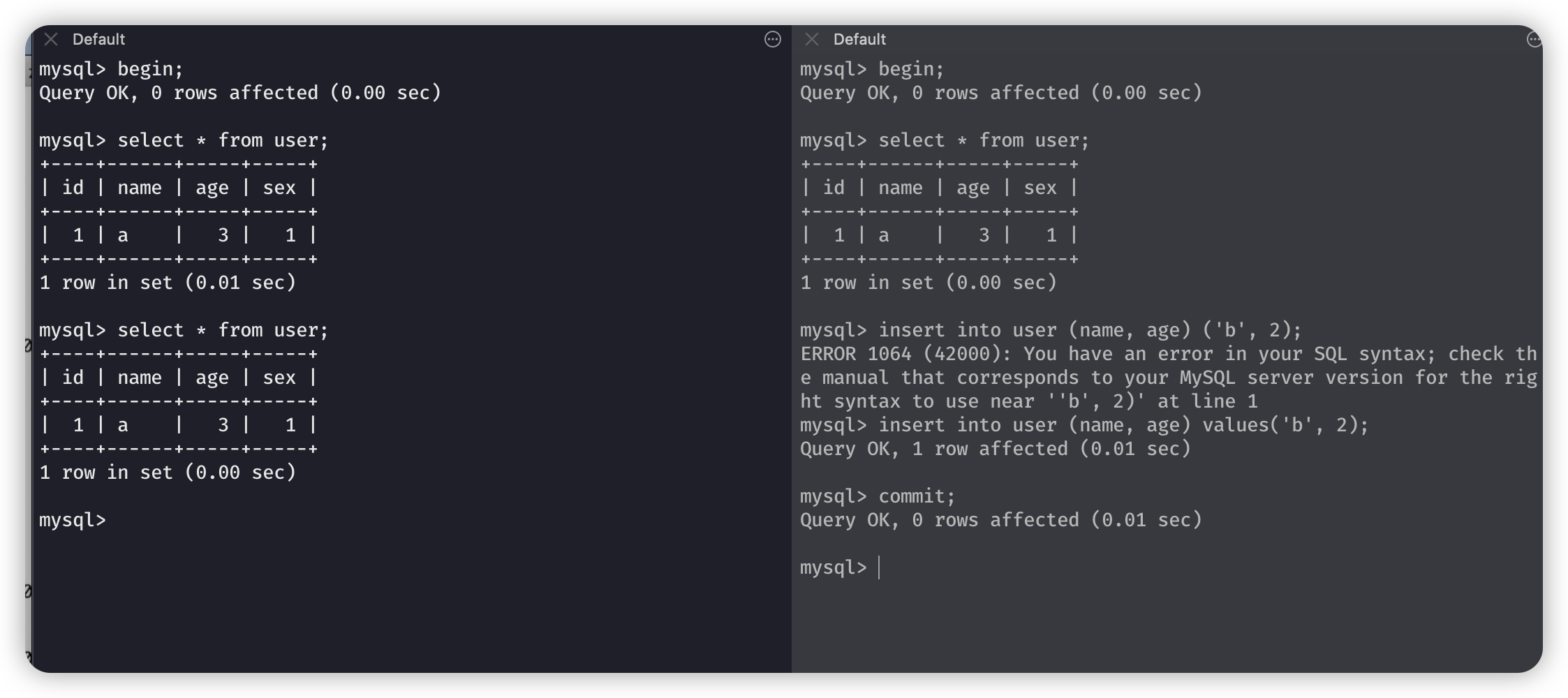
产生了幻读
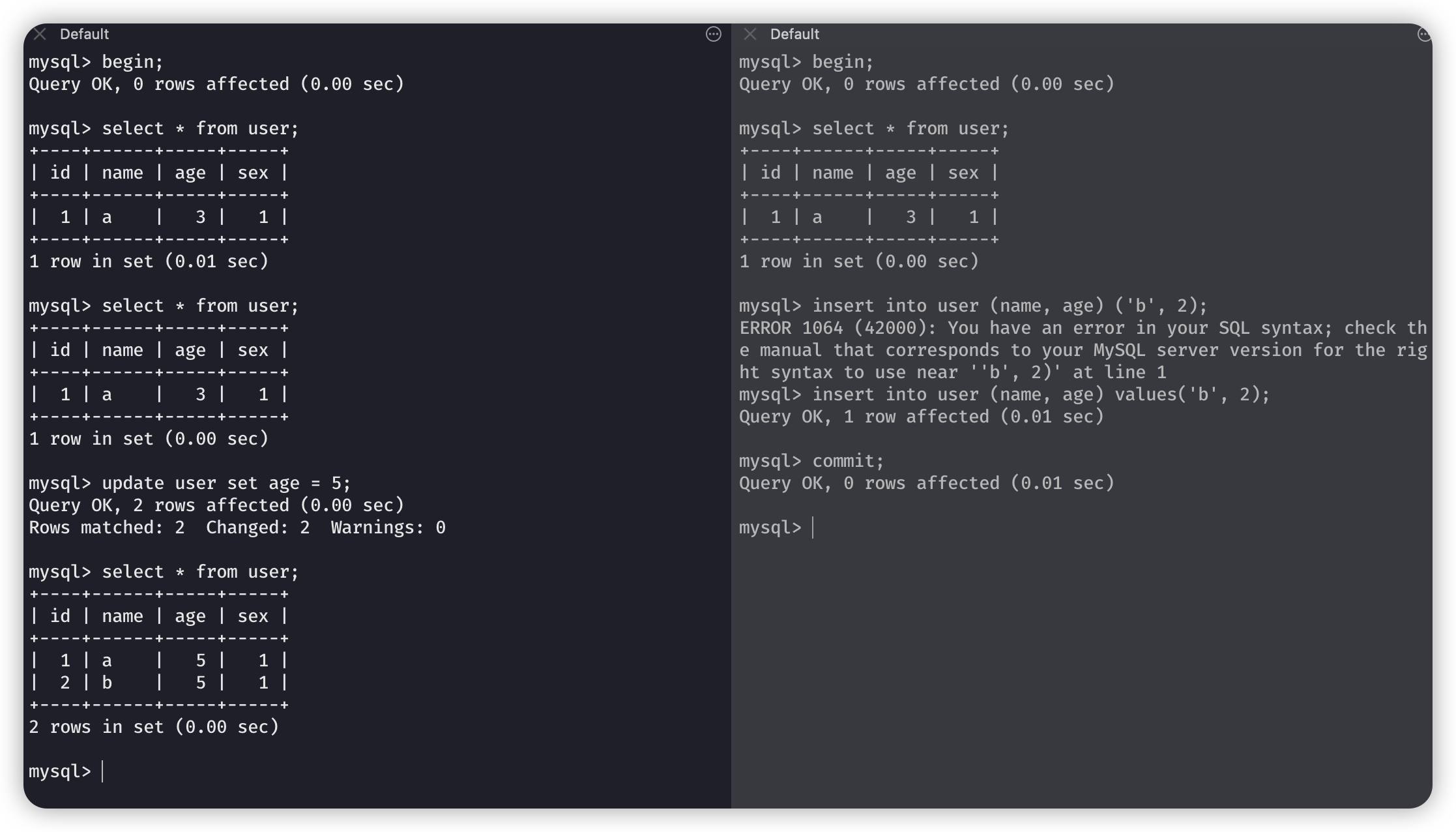
当左边再次执行了update操作,就是当前读,执行了当前读的时候,就不是第一次快照读的数据了;然后再次查询就会查询到最新的数据了。
解决:
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from user for update;
+----+------+-----+-----+
| id | name | age | sex |
+----+------+-----+-----+
| 1 | a | 5 | 1 |
| 2 | b | 5 | 1 |
+----+------+-----+-----+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show engine innodb status\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Type: InnoDB
Name:
Status:
=====================================
2022-09-21 22:33:54 0x16e48b000 INNODB MONITOR OUTPUT
=====================================
Per second averages calculated from the last 1 seconds
-----------------
BACKGROUND THREAD
-----------------
srv_master_thread loops: 8 srv_active, 0 srv_shutdown, 2059 srv_idle
srv_master_thread log flush and writes: 2067
----------
SEMAPHORES
----------
OS WAIT ARRAY INFO: reservation count 79
OS WAIT ARRAY INFO: signal count 79
RW-shared spins 0, rounds 38, OS waits 18
RW-excl spins 0, rounds 25, OS waits 0
RW-sx spins 0, rounds 0, OS waits 0
Spin rounds per wait: 38.00 RW-shared, 25.00 RW-excl, 0.00 RW-sx
------------
TRANSACTIONS
------------
Trx id counter 3165204
Purge done for trx's n:o < 3165203 undo n:o < 0 state: running but idle
History list length 3
LIST OF TRANSACTIONS FOR EACH SESSION:
---TRANSACTION 281479883066040, not started
0 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 0 row lock(s)
---TRANSACTION 3165203, ACTIVE 10 sec
2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 3 row lock(s)
MySQL thread id 2, OS thread handle 6145224704, query id 58 localhost root starting
show engine innodb status
--------
FILE I/O
--------
I/O thread 0 state: waiting for i/o request (insert buffer thread)
I/O thread 1 state: waiting for i/o request (log thread)
I/O thread 2 state: waiting for i/o request (read thread)
I/O thread 3 state: waiting for i/o request (read thread)
I/O thread 4 state: waiting for i/o request (read thread)
I/O thread 5 state: waiting for i/o request (read thread)
I/O thread 6 state: waiting for i/o request (write thread)
I/O thread 7 state: waiting for i/o request (write thread)
I/O thread 8 state: waiting for i/o request (write thread)
I/O thread 9 state: waiting for i/o request (write thread)
Pending normal aio reads: [0, 0, 0, 0] , aio writes: [0, 0, 0, 0] ,
ibuf aio reads:, log i/o's:, sync i/o's:
Pending flushes (fsync) log: 0; buffer pool: 0
1270 OS file reads, 167 OS file writes, 96 OS fsyncs
0.00 reads/s, 0 avg bytes/read, 0.00 writes/s, 0.00 fsyncs/s
-------------------------------------
INSERT BUFFER AND ADAPTIVE HASH INDEX
-------------------------------------
Ibuf: size 1, free list len 0, seg size 2, 0 merges
merged operations:
insert 0, delete mark 0, delete 0
discarded operations:
insert 0, delete mark 0, delete 0
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 2 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 34679, node heap has 2 buffer(s)
0.00 hash searches/s, 0.00 non-hash searches/s
---
LOG
---
Log sequence number 583228139
Log flushed up to 583228139
Pages flushed up to 583228139
Last checkpoint at 583228130
0 pending log flushes, 0 pending chkp writes
62 log i/o's done, 0.00 log i/o's/second
----------------------
BUFFER POOL AND MEMORY
----------------------
Total large memory allocated 137428992
Dictionary memory allocated 105920
Buffer pool size 8192
Free buffers 7646
Database pages 542
Old database pages 219
Modified db pages 0
Pending reads 0
Pending writes: LRU 0, flush list 0, single page 0
Pages made young 0, not young 0
0.00 youngs/s, 0.00 non-youngs/s
Pages read 503, created 39, written 83
0.00 reads/s, 0.00 creates/s, 0.00 writes/s
No buffer pool page gets since the last printout
Pages read ahead 0.00/s, evicted without access 0.00/s, Random read ahead 0.00/s
LRU len: 542, unzip_LRU len: 0
I/O sum[0]:cur[0], unzip sum[0]:cur[0]
--------------
ROW OPERATIONS
--------------
0 queries inside InnoDB, 0 queries in queue
0 read views open inside InnoDB
Process ID=37523, Main thread ID=6139408384, state: sleeping
Number of rows inserted 2, updated 4, deleted 0, read 24
0.00 inserts/s, 0.00 updates/s, 0.00 deletes/s, 0.00 reads/s
----------------------------
END OF INNODB MONITOR OUTPUT
============================
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified
mysql>
同时的右边
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>
上面左边就上了锁。
然后右边在进行更新操作就会卡住等待
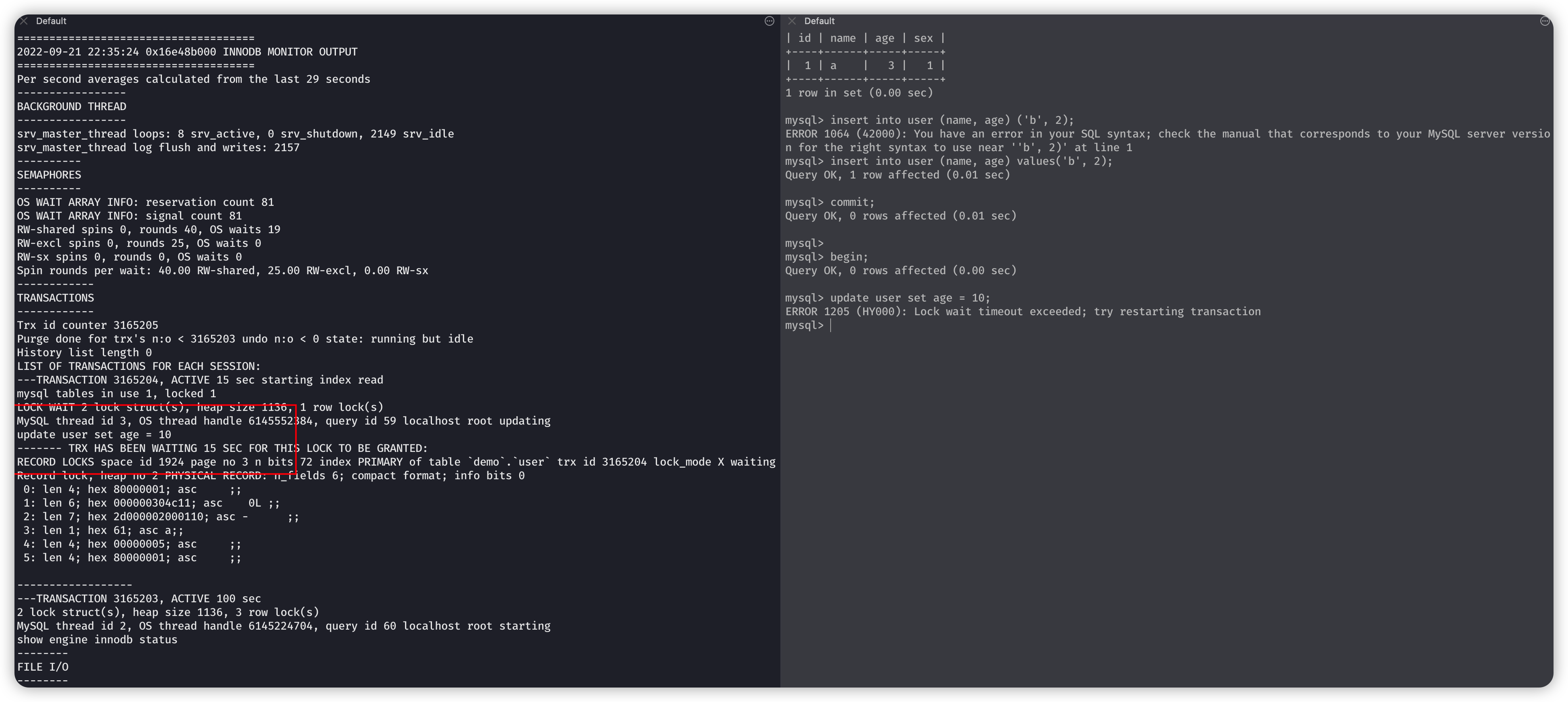
这样就操作不了更新,就不会产生幻读。
redolog
用来保证事务的持久性的,保证数据不会丢失的。
问题:既然有了
redolog,为什么还要有binlog?
原因
redolog:是因为innodb才有的
binlog:是整个 MySQL 服务就有,别的存储引擎也有
问题:既然 2 个都有,那么怎么保证数据的一致性?
看一个两阶段提交的示例图
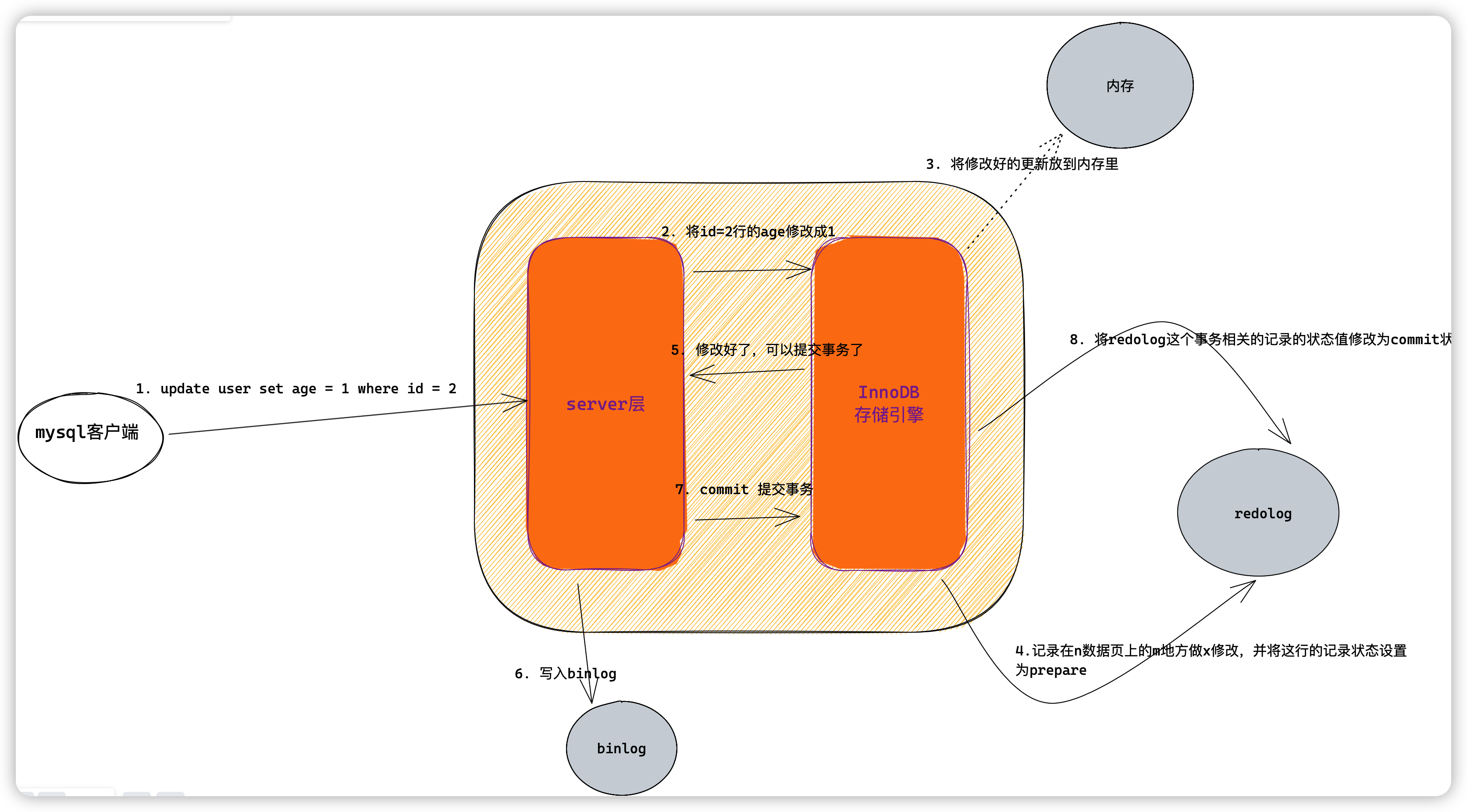
恢复数据的时候使用binlog和redolog两部分数据进行比较就可以了。
总结
事务有几个属性
- 原子性是使用
undolog实现的 - 隔离性是使用
MVCC实现的 - 持久性是使用
redolog实现的 - 一致性,是使用上面的 3 个共同保证的。
